Root Canal Treatment
Have you ever felt a pang in one of your teeth after drinking, this indications that you have an infected tooth and might need root canal treatment. These infections do not resolve on their own, so if you are experiencing continuous tooth discomfort, you should consult a dentist.
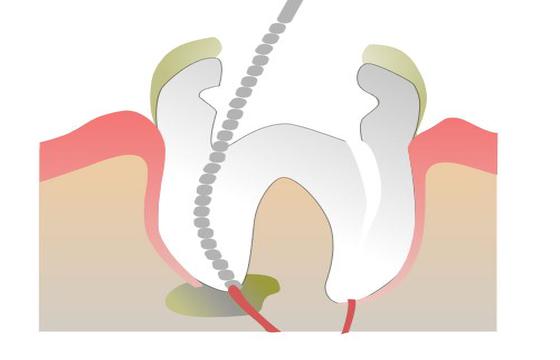
What is Root Canal Treatment
This is a dental operation that treats infection or damage to the pulp of a tooth. The pulp is a soft tissue found in the core of the tooth that contains nerves, blood vessels and connective tissues. If you require, your dentist or endodontist will describe the procedure so that you understand what to expect.
How long time takes of Root Canal Treatment Process
The length of process varies based on a number of factors, including the intricacy of the tooth's architecture, the depth of the infection or damage and the specific dentist's method. However, in average, consultation can last between 60 and 90 minutes.
Stages are, First diagnosis take 10 to 20 minutes, Anesthesia, Access and Cleaning take approximately 30 to 60, Filling takes about 20 to 30 minutes.
Types of Root Canal Treatments
There are basically two forms of treatment,
Conventional(surgical) Root Canal Treatment
This is the typical root canal technique. General steps detailed below,
Access Opening, the dentist or endodontist creates an opening in the tooth's crown to gain access to the pulp chamber.
Cleaning and Shaping, specialized devices are used to remove infected or damaged pulp tissue from the teeth's root canals. The canals are then shaped to make them ready for filling.
Disinfection, are cleaned and disinfected to remove bacteria and prevent future infections.
Filling, the cleansed and formed canals are sealed with gutta-percha, a biocompatible substance that prevents recontamination.
Restoration, following treatment, the tooth's access opening is filled with a temporary or permanent filling. In many circumstances, a dental crown is used to restore the tooth's strength and function.
Non-Surgical Root Canal Treatment
Before deciding on a surgical option, a non-surgical treatment may be tried. This procedure follows the same procedures as traditional ways, but it is administered via the tooth's crown, eliminating the need for surgical intervention. If the non-surgical does not fix the problem, surgical treatments like as apicoectomy (removal of the tooth's tip) may be pursued.
Both methods are intended to save the natural tooth by removing infected or damaged pulp tissue, cleaning and sealing them to avoid reinfection. The choice between traditional and non-surgical treatment depends on factors such as the degree of the infection, the state of the tooth and the patient's overall oral health.
Process of Root Canal Treatment
Here's a thorough explanation of the procedure,
Diagnoses and assessments, the dentist begins by inspecting the patient's teeth and evaluating their dental history. X-rays can be used to detect the level of damage and the anatomy of the tooth's roots.
Anesthesia, local anesthesia is used to numb the tooth and surrounding tissues, ensuring that the patient is comfortable throughout the treatment.
Access and isolation, once the tooth is numb, the dentist isolates it with a rubber dam, which keeps it dry and saliva-free during the treatment. The dentist next drills an incision in the tooth's crown to provide access to the pulp chamber.
Pulp Removal, specialized equipment, such as files and reamers, are used to extract infected or inflamed pulp tissue from the pulp chamber. The canals are cleaned and shaped to eliminate trash and microorganisms.
Irrigation and disinfection, They are irrigated with antimicrobial treatments to disinfect and eliminate any leftover debris or bacteria. This phase contributes to the elimination of infection and minimizes the chance of reinfection.
Filling the canals, canals are cleaned and formed before being filled with gutta-percha, a biocompatible substance. Gutta-percha is coupled with a sealing cement to prevent microorganisms from entering and contaminating the canals. Sealing the Access Opening. After the canals have been filled, the access opening in the tooth's crown is sealed with a temporary or permanent filling material.
Restoration, in many circumstances, the tooth may need additional repair, such as a dental crown, to regain its strength, function and appearance. The dental crown is custom-made to fit the treated tooth's shape and size and it is cemented over the remaining tooth structure.
Follow-Up, after treatment is completed, the patient may need to arrange a follow-up appointment to monitor the healing process and ensure that the therapy was effective. Regular dental check-ups and proper oral hygiene habits are vital for the health of the treated tooth and surrounding tissues.
Alternatives of Root Canal Treatment
There are numerous alternatives to treatments available, depending on the exact scenario and condition of the tooth,
Extraction, if the tooth has been significantly damaged or infected and cannot be saved, extraction may be required. Once extracted, the tooth might be replaced with dental implants, bridges, or partial dentures.
Pulpotomy, in some circumstances, particularly in children, a pulpotomy may be used instead of this. This entails removing the diseased pulp while leaving the healthy pulp intact.
Antibiotics can be provided to cure the infection temporarily, but this is not a permanent solution to the underlying problem.
Apicoectomy is a surgical technique that removes the tip of the tooth's root, along with the affected tissue, rather than the complete tooth.
Regenerative Endodontics is a new field that seeks to restore tooth pulp tissue rather than eliminating it entirely. It entails procedures that promote the regrowth of pulp tissue in the tooth.
Monitoring and Preventive Care, if the infection is not severe, the tooth may be continuously watched through frequent dental check-ups and preventive care to ensure that it remains stable and does not worsen.
The choice of alternative treatment is determined by several criteria, including the severity of the infection, the state of the tooth and the patient's overall oral health goals.
Frequently asked questions about Root Canal Treatment
*The treatment pages provided on this platform are intended for informational purposes only and do not constitute medical or dental advice, diagnosis, or treatment recommendations. The information presented on these pages is not a substitute for professional medical or dental advice from qualified healthcare providers.
*By accessing and using the treatment pages on this platform, you acknowledge and agree to the terms of this disclaimer. If you do not agree with these terms, please refrain from using the treatment pages.