Apical Resection
Even after receiving a root canal treatment and you still feel pain or discomfort, apical resection surgery could be beneficial to you. Here is a guide of surgery, how it's done and why it might be required for your oral health in this post.
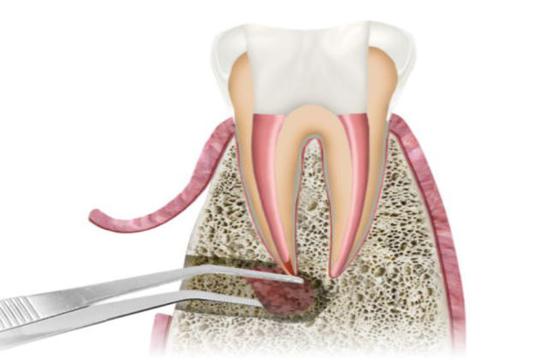
What is Apical Resection
Dental surgery known as apicoectomy or apical excision, is carried out when a root canal therapy is unable to heal an infection or inflammation at the tooth's apex or root tip. When other therapies, such root canal retreatment are impractical or have not been effective in curing the infection, apical excision is usually taken into consideration. An endodontist, a dentist with expertise in addressing problems pertaining to the tooth pulp and root canal system, frequently performs it. In a root canal operation, the dentist or endodontist cleans, forms and fills the canal space to stop future infection after removing infected or inflammatory pulp from the tooth's internal chamber and canals.
How long time takes of Apical Resection Process
The intricacy of the case, the location of the damaged tooth, and the particular circumstances of the patient can all determine how long an operation takes. Operations normally take between thirty and sixty minutes to finish. Remember that these time estimates are only estimates that may change based on the particulars of each case as well as the expertise and experience of the endodontist or dentist doing the treatment.
Process
Apical resection or apicoectomy, is a multi-step procedure that is usually carried out by an endodontist or dentist. An outline of the process is provided below,
Evaluation and Diagnosis, the dentist or endodontist will examine the patient's dental history, symptoms, and past dental procedures prior to carrying out. They could also use imaging investigations or X-rays as diagnostic procedures to evaluate the state of the tooth and its surrounding tissues.
Anesthetic, to make sure the patient is comfortable throughout the surgery and to numb the region surrounding the damaged tooth, local anesthetic is delivered. To aid in the patient's relaxation, the dentist may occasionally additionally provide sedation or other types of anesthetic.
Accessing the Root Tip, the dentist exposes the root tip by making a tiny incision in the gum tissue next to the tooth after numbing the region. A little flap of gum tissue may occasionally be lifted to improve access to the underlying tissues.
Extracting Infected Tissue, the dentist meticulously removes any inflammatory or infected tissue from the tooth's root tip. This could also require trimming off a tiny piece of the root tip.
Cleaning and Sealing the Root Tip, the dentist cleans the inside of the root tip to make sure that no germs or debris are left behind after extracting the contaminated tissue. In order to stop more infection, the root tip is then sealed with a biocompatible substance.
Suturing the Gum Tissue, to encourage healing and guarantee a strong closure, the dentist sutures the gum tissue back into place after sealing the root tip.
The directions for After surgery Care, following the treatment, the dentist gives directions on how to manage discomfort and swelling, consume soft foods and take care of your teeth. In order to assist patients manage their discomfort and avoid infection, doctors may also give antibiotics or painkillers.
Follow-up, in order to track their recovery and make sure their teeth are working correctly, patients usually schedule a follow-up consultation. Sometimes other dental procedures, such putting in a dental crown or filling, are required to restore the tooth's structure and function.
Who need Apical Resection Treatment?
If a patient has had prior root canal therapy but still has ongoing infections or inflammation in the apex of their tooth, apicoectomy, , may be advised.
Persistent Infections, in the root tip of a tooth, some infections may continue or come back even after receiving root canal therapy. The afflicted region may experience discomfort, swelling and soreness as a result of these illnesses. The dentist can eliminate the infection's cause and encourage recovery.
Root Canal Failure, in certain situations, problems with the root canal system may not be fully resolved by root canal therapy. This may be the result of things like poorly cleaned and sealed canals, overlooked canals or intricate canal morphology. Offers a chance to deal with these unsolved problems at the very tip of the root.
Dental Trauma, the root structure of a tooth can be harmed and its overall health compromised by traumatizing injuries to the tooth, such as fractures or dislodgments. May be required to remove the injured tissue and stop additional problems if the trauma damages the root tip and causes infection or inflammation.
Resorption, the disintegration and loss of tooth structure, especially the root, is caused by the body's normal processes. The integrity of the tooth may be compromised by internal or external root resorption, which may also exacerbate infections or other dental issues. To treat resorption at the root tip and protect the tooth, may be necessary.
Persistent Symptoms, more testing may be necessary to identify the underlying reason in patients who still suffer symptoms like pain, swelling or sensitivity in a tooth that has already had treatment. Treatment of problems affecting the root tip, which may be causing these symptoms, can be focused with treatment.
Benefit and Risks
Apical resection provides a number of possible advantages for those who are coping with recurrent infections or inflammation at the tooth's apex or root tip. An outline of the advantages and disadvantages of surgery is provided below,
Benefits
Preservation of Natural Tooth, by treating problems at the root tip, preserve the natural tooth. Since keeping natural teeth is typically preferable to extraction and replacement choices, this aids in maintaining oral function, aesthetics and general dental health.
Resolution of Infections, surgery can successfully cure chronic infections that might not respond to conventional therapies like root canal therapy by removing infected or inflammatory tissue and sealing the root tip. This may result in the afflicted area's discomfort, swelling and tenderness being relieved over time.
Preventing Additional Damage, lowers the chance of complications such abscesses, bone loss, and systemic infections by stopping the infection from spreading to neighboring teeth and tissues. The process encourages healing and aids in the restoration of dental health by treating problems at the root tip.
Better Oral Health, treating infections and inflammation at the root tip improves oral health in general and may avert the need for more involved dental procedures in the road. Patients can benefit from years of healthy teeth and gums after surgery.
Risks
Surgical risks, has inherent hazards, such as bleeding, infection, and tissue injury, just like any other surgical treatment. Nonetheless, these risks are usually negligible and may be reduced with appropriate pre and post-operative care.
Potential issues, after surgery, issues such nerve injury, sinus perforation, and insufficient healing are possible but are rare. These issues may necessitate further procedures and lengthen the healing period.
Post-operative Pain, after surgery, patients may have slight pain, bruising and swelling. However, painkillers, cold packs, and other conservative methods can be used to alleviate these symptoms, which are often transient.
Long-term Success Rates, although surgery is quite effective in curing infections and saving teeth, there is a little chance that it may fail or return later on. In order to monitor the condition of the treated tooth and avoid issues down the road, routine dental checkups and care are crucial.
How to care After Surgery
Following surgery, self-care is essential for encouraging recovery, averting problems, and guaranteeing the procedure's success. The following are some crucial pointers for post-operative management after surgery:
Observe Instructions, you will get personalized post-operative instructions from your oral surgeon or dentist, based on your unique requirements. To maximize your recovery and reduce the chance of problems, you must carefully adhere to following guidelines.
Handle pain, following surgery, some pain, swelling and bruising are typical. Use over-the-counter analgesics if needed, and take any prescribed painkillers exactly as indicated. The outside of your face close to the surgery site might benefit from using cold packs to minimize swelling and pain.
Rest and Relaxation, after surgery, schedule a few days of rest and relaxation. Steer clear of taxing exercises, hard lifting, and intense activities that might impede healing or exacerbate bleeding. Your body will heal itself more quickly if you get enough sleep and relax.
Maintain Dental cleanliness, maintaining dental cleanliness is essential to avoiding infection and accelerating recovery. To prevent interfering with the healing process, however exercise gentleness around the surgery site. For the first few days following surgery, you might be told not to brush or floss in the vicinity of the incision.
Dietary Guidelines, to prevent aggravating the surgical site, limit your intake to soft, bland meals in the initial days after surgery. Choose meals like smoothies, yogurt, soup and mashed potatoes that are simple to chew and swallow. Avert anything that might irritate the surgical site, such as hot, spicy, acidic or crunchy meals.
Keep Yourself Hydrated, to keep hydrated and aid in healing, consume lots of liquids. The best option is water, but you can also drink other clear beverages including broth, diluted fruit juice and herbal tea.
Avoid alcohol and smoke, these substances might impede the healing process and raise the possibility of problems. To encourage the best possible healing throughout the recovery phase, abstain from smoking and consume little alcohol.
Attend Follow-up Appointments, make sure you show up for any planned follow-up consultations with your oral surgeon or dentist. During these visits, your doctor can check on you, take out sutures if needed and handle any issues or problems that might come up.
Keep an Eye Out for Complications, although problems following apical resection surgery are uncommon, it's important to recognize the warning signals, which include heavy bleeding, excruciating pain, prolonged swelling, fever or strange discharge from the surgical site. If you encounter any of these symptoms, get in touch with your oral surgeon or dentist right once.
Frequently asked questions about Apical Resection
*The treatment pages provided on this platform are intended for informational purposes only and do not constitute medical or dental advice, diagnosis, or treatment recommendations. The information presented on these pages is not a substitute for professional medical or dental advice from qualified healthcare providers.
*By accessing and using the treatment pages on this platform, you acknowledge and agree to the terms of this disclaimer. If you do not agree with these terms, please refrain from using the treatment pages.