Gum Graft Surgery
A lack of color indicates that the gum graft has lost blood flow and is dying. When your gingivitis graft failed, you will most likely observe a significant area of white tissue coming off your tooth. If you see this or have additional concerns such as changes in the appearance of your gums, redness, swelling or inflammation pus at the surgery site or tooth roots can cause pain or discomfort, you need immediate assistance.
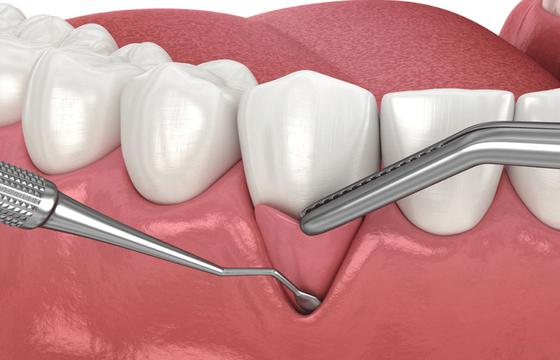
What is Gum Graft Surgery
Often called gingival graft surgery, is a dental operation used to cure gum recession. Gum recession occurs when the gum tissue around the teeth fades away or pulls back, exposing more of the tooth and possibly the root. If not treated, this can cause tooth sensitivity, increased decay risk and possibly tooth loss. Recovery is usually associated with considerable discomfort and swelling and patients may be required to follow special post-operative care guidelines, such as avoiding certain foods and practicing good dental hygiene.
How long time takes of Gum Graft Surgery Process
First visit is the stage of consultation and preparation. Your dentist schedule an appointment. Surgery usually takes one to two hours, depending on the complexity. The appointments may take place at regular intervals over several weeks or months, depending on your development. While the first recuperation period may be a few weeks, it can take several months for the full effects of the treatment to show. During this period, the grafted tissue will progressively merge with your natural gum tissue, providing additional coverage and protection for the tooth roots.
Types of Gum Graft Surgery
Connective tissue graft, in this frequent procedure, the surgeon makes an incision in the palate and takes tissue beneath the top layer. This tissue is then sewn to the receding gum.
Free gingival graft, similar to the connective tissue transplant, tissue is extracted from the palate, but from the surface rather than beneath the top layer.
Pedicle graft, Instead of extracting tissue from the palate, tissue near the receding gum is used. This tissue stays partially linked to its original location and rotates over the receding area.
Procedures
The duration of treatment varies depending on a number of factors, including the severity of gum recession, the type of graft surgery used and individual recovery timeframes. Generally, the procedure consists of multiple stages:
Consultation, your periodontist or oral surgeon will examine your gums and teeth to identify the extent of gum recession and the best treatment approach. During this session, the dentist will explain the procedure to you and answer any questions or concerns you may have.
Preparation, prior to gum transplant surgery, you may need to have your teeth and gums thoroughly cleaned, as well as address any underlying gum disease or other oral health issues.
Surgery, normally takes 1 to 2 hours, depending on the complexity of the treatment and the amount of grafts needed. During the procedure, the periodontist will harvest tissue from the palate or another donor site and graft it to the receding gum area. To decrease discomfort, the patient is frequently sedated or given local anesthesia throughout the surgery.
The recovery period after surgery varies from person to person. Initially, you may feel discomfort, edema and small bleeding at the graft site. Most patients can resume their normal activities after a day or two, although they should avoid excessive physical activity for a week or more. It is critical to closely follow your dentist's post-operative instructions, which may include dietary restrictions, pain management measures and oral hygiene requirements.
Follow-up appointments, your dentist will schedule follow-up sessions to check the healing process and verify that the grafts are properly integrated into your existing gum tissue. These appointments may take place at regular intervals over several weeks or months, depending on your development.
Who needs Gum Graft Surgery?
Gum recession is a condition where the gum tissue wears away, exposing the teeth's roots. Surgery is usually advised for these patients. A number of things can lead to a gum recession such as,
Periodontal disease, as it erodes the tooth's supporting tissues, advanced gum disease can cause gum recession. Aggressive brushing, overly vigorous brushing or using a toothbrush with firm bristles can gradually erode gum tissue.
Genetics, a person's tendency toward thin or inadequate gum tissue may run in the family.
Misaligned teeth, Excessive pressure on specific gum regions can result in gum recession if teeth are positioned too tightly together or are misaligned.
Damage, Gum recession may arise from physical damage to the teeth or gums.
Bruxism, consistently grinding your teeth can cause gum recession. Gum recession can cause dental sensitivity, a higher chance of tooth decay and possibly even tooth loss if it is not corrected.
Frequently asked questions about Gum Graft Surgery
*The treatment pages provided on this platform are intended for informational purposes only and do not constitute medical or dental advice, diagnosis, or treatment recommendations. The information presented on these pages is not a substitute for professional medical or dental advice from qualified healthcare providers.
*By accessing and using the treatment pages on this platform, you acknowledge and agree to the terms of this disclaimer. If you do not agree with these terms, please refrain from using the treatment pages.