Gum Disease Treatment
Periodontal disease often known as gum disease, is a widespread yet avoidable illness that affects a large number of people globally. It can range from moderate gum inflammation (gingivitis) to more severe types (periodontitis). If not taken care of, can result in tooth loss. Maintaining dental health and general well-being requires understanding the reasons, identifying the symptoms, and learning how to prevent it.
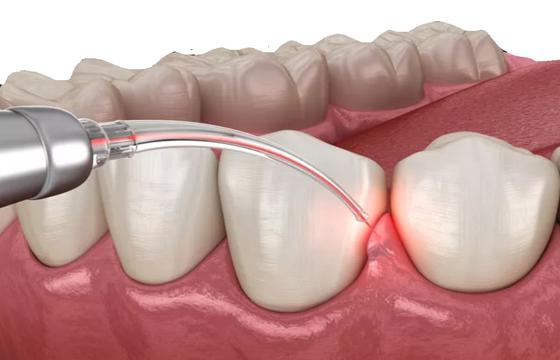
What is Gum Disease Treatment
Gum disease is an inflammation of the soft tissues (gums) around the teeth. It is the buildup of tartar and plaque around the teeth that causes this condition. Bacteria and food remnants combine to produce plaque, a sticky coating. If plaque is not routinely removed, tartar may develop, hardening and mineralizing over time. The gums can get infected and irritated by both plaque and tartar.
How long time takes of Gum Disease Treatment Process
The length of time needed to treat varies based on the severity of the condition and the selected course of action. Professional cleaning and regular at-home care may generally cure mild gingivitis in a few of weeks, however scaling and root planing for early to moderate periodontitis may need many visits over several weeks to months in order to fully recover. Surgical procedures may be necessary for advanced periodontitis; initial healing may take a few weeks, and total regeneration may take months or even a year.
Symptoms of Gum Disease
Early Stage Gingivitis
Red, swollen or tender gums.
Gums that bleed easily, especially during brushing or flossing.
Persistent bad breath (halitosis).
Receding gums.
Formation of small pockets between teeth and gums.
Advanced Stage Periodontitis
Every gingivitis symptom, but more noticeable Pus between teeth and gums.
Alterations in how teeth come together during chewing.
Slipping or loose teeth. Modifications to partial denture fit.
Persistently unpleasant aftertaste. Obvious pus near the mouth and teeth.
Teeth elongation or gum recession. Deep grooves between the gums and teeth.
Bone loss, which can be shown on X-rays of the teeth.
Process
Professional dental cleaning, include cleaning the teeth and gums of plaque and tartar, which is hardened plaque. Must be prevented and treated with regular dental cleanings.
In order to assist stop germs from reattaching, scaling and root planing is a deep cleaning process that entails removing plaque and tartar from both above and below the gum line as well as smoothing out rough places on the tooth roots. To ensure comfort, local anesthetic may be used during this treatment, which may need to be done across several visits.
Antibiotic Treatment, to assist manage bacterial infection and lessen inflammation, doctors may give antibiotics in the form of mouthwashes, gels or oral pills.
Surgical Treatments, to restore destroyed gum tissue and bone, surgical treatments may be required in more advanced forms. These might consist of:
In order to lessen the depth of the pocket, flap surgery involves removing the gums to remove tartar deposits and then reattaching the gum tissue.
Bone grafts, used to rebuild or replace bone that has damaged.
Soft Tissue Grafts, to conceal exposed tooth roots and improve the look of the gumline, tissue from another area of the mouth is taken or synthetic material is used.
Laser Therapy, some dentists use laser technology to stimulate the regeneration of gum tissue while eliminating germs and diseased tissue.
Why Gum Disease happens?
Buildup of Plaque, on teeth plaque is a sticky layer of germs that is always present. If plaque is not eliminated by practicing good dental hygiene, such as brushing and flossing, it can solidify into tartar, also known as calculus, which is more challenging to remove and can irritate the gums, eventually resulting.
Bad Dental Hygiene, if plaque and tartar are not removed by brushing and flossing enough, they can ultimately build up along the gum line and cause gingivitis, which can become periodontitis if untreated.
Smoking and Tobacco Use, smoking impairs immunity, which makes it more difficult for the body to fight off infections. Additionally, smoking lowers blood flow to the gums, increasing their susceptibility to infection and impeding their ability to recover.
Genetics, certain people may have a higher hereditary susceptibility. Genetics can affect a person's vulnerability by influencing things like immune system strength and the anatomy of the gums and teeth.
Certain Medical Conditions, the body's capacity to fight infection might be compromised by systemic conditions including diabetes, autoimmune disorders and HIV/AIDS, which raises the risks. Additionally, hormonal shifts that occur throughout adolescence, pregnancy and menopause can exacerbate gum sensitivity and inflammation.
Certain Medications, some medications like some immunosuppressants, calcium channel blockers, and anticonvulsants, can cause gingival hyperplasia, or the overgrowth of gum tissue or they can reduce saliva flow, which can cause dry mouth and raise the risks.
Poor Nutrition, a diet heavy in sugar and carbs raises the risks by promoting the accumulation of plaque. Vitamin C deficiency in particular can weaken gums and increase their susceptibility to infection.
How to avoid
By choosing a healthy lifestyle and practicing proper oral hygiene.
Brush Your Teeth Twice a Day, spend two minutes thoroughly brushing your teeth twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Plaque and food particles are removed from your teeth's surfaces as well as the gum line when you brush.
Floss Every Day, flossing helps get rid of food particles and plaque that your toothbrush could miss from in between your teeth and along the gum line. Be careful when flossing to prevent gum damage.
Use Mouthwash, to help lessen plaque and bacteria that cause gingivitis, rinse your mouth with an antimicrobial mouthwash. Seek for mouthwashes with fluoride or antimicrobial components like chlorhexidine.
Keep a Balanced Diet, reducing your intake of sugary foods and drinks will help prevent plaque development and lower your chance of developing. Rather, choose a diet that is well-balanced and abundant in whole grains, dairy products, fruits, vegetables and lean meats.
Stop Smoking, smoking raises your risks and can make it harder for your body to repair and fight off infections. For the sake of your general and oral health, you should think about giving up smoking and using tobacco products.
See your dentist on a regular basis, make an appointment for routine dental cleanings and examinations at least twice a year, or as advised by your dentist. Plaque and tartar accumulation that cannot be eliminated by routine brushing and flossing are removed by professional cleanings. Additionally, your dentist can identify early indicators of gum disease and administer the necessary care.
Keep Your Dental Health, observe any changes in your gums, like bleeding, swelling, redness or receding gums. See your dentist right away for an assessment and treatment if you have any symptoms, such as loose teeth or chronic foul breath.
Handle Stress, stress can exacerbate inflammation throughout the body, including the gums and impair immunity. Engage in stress-reduction practices to support general health and assist manage stress, such as deep breathing, exercise, meditation or hobbies.
Frequently asked questions about Gum Disease Treatment
*The treatment pages provided on this platform are intended for informational purposes only and do not constitute medical or dental advice, diagnosis, or treatment recommendations. The information presented on these pages is not a substitute for professional medical or dental advice from qualified healthcare providers.
*By accessing and using the treatment pages on this platform, you acknowledge and agree to the terms of this disclaimer. If you do not agree with these terms, please refrain from using the treatment pages.