Bone Grafting
The surgical technique known as bone grafting has completely changed the fields of maxillofacial, orthopedic and dental surgery. It is an essential method for bone development promotion, bone defect repair and healing support in a variety of medical diseases. The purpose of this page is to examine the complexities including its uses, methods, kinds of grafts and overall procedure.
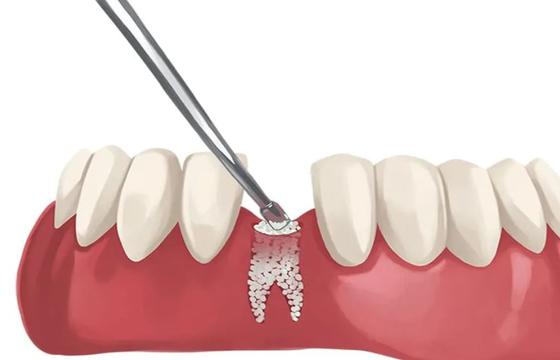
What is Bone Grafting
A surgical technique called bone grafting is performed to restore lost bone or treat fractures that don't mend well. It entails transferring bone tissue to a location that needs bone, either by autograft from one part of the body or by allograft from a donor. Stimulating bone regeneration and promoting healing in locations where bone has been lost or injured as a result of trauma, illness or other circumstances is the aim of bone seeding.
How long time takes of Bone Grafting Process
The actual surgery, which includes anesthesia, graft preparation, graft implantation and graft harvesting (if necessary), usually takes a few hours. However, it may take many months for the graft to fully integrate and recuperate. Patients get post-operative treatment during this period, which includes pain management, activity limitations and follow-up sessions to track the status of recovery.
Reasons of Bone Grafting
Oral and maxillofacial surgery, orthopedic surgery and other medical specialties frequently carry out bone grafting treatments.
Fracture Healing, can aid in the healing of fractures, such as nonunion fractures or fractures with substantial bone loss, that are difficult for the body to fix on their own.
Bone Regeneration, can aid in the regeneration of lost bone tissue and the restoration of bone strength and function in situations of bone loss brought on by trauma, infection or illness (such as osteoporosis).
Dental Implants, in order to prepare the jawbone for the implantation of dental implants, is frequently done in dentistry. Procedure may be required to give the implants the proper support since insufficient bone volume in the jaw might jeopardize their success.
Spinal fusing, to encourage the fusing of two or more vertebrae, commonly employed in spinal fusion procedures. Spinal fusion is a treatment for degenerative disc degeneration and spinal instability that stabilizes the spine by promoting the creation of new bone between neighboring vertebrae.
Which Sources used for Treatment?
Individuals can obtain bone transplants from a number of sources such as,
Autorafts, made from the patient's own body, usually the iliac crest of the hip, ribs or other bones.
Allografts, from donors acquired from tissue banks or cadavers.
Xenografts, Bone tissue sourced from animals other than humans, such pig or cow bone.
Following transplantation, acts as a scaffold for the formation of new bone, eventually fusing with the surrounding bone tissue.
Procedures
There are several phases in treatment procedure, ranging from pre-operative assessment to post-operative care.
Pre-operative Assessment, Medical History and Physical Exam, the patient's medical history is examined, taking into account any underlying illnesses or prescription drugs. A physical assessment and imaging tests, such CT or X-rays, can be used to determine the degree of bone loss or injury.
Treatment Planning, the surgeon chooses the surgical technique, the kind of bone transplant that is required and its source, whether it be an autograft, allograft or xenograft, based on the evaluation.
Surgical Procedure,
Anesthesia, depending on the intricacy of the operation and the patient's request, the patient is either put under general anesthesia, which renders them unconscious or local anesthetic combined with sedation, which leaves them awake but comfortable.
Graft Harvesting, in the event that an autograft is being used, bone marrow is taken from a donor site, such as the iliac crest on the hip, or from another appropriate region on the patient's body. A portion of bone tissue is carefully removed by the surgeon after making an incision at the donor location.
Graft Preparation, to prepare the collected bone tissue for transplantation, extra soft tissue and debris are usually removed and the tissue is shaped to match the defect location.
Closure, a sterile bandage is placed to the surgical site and the wounds are sealed with stitches or surgical staples.
Post-operative Care, Pain Management, medication is given to patients to alleviate discomfort following surgery.
Activity Restrictions, in order to promote adequate healing, patients may be recommended to minimize physical activity and refrain from applying weight to the treated region.
Follow-up Visits, patients usually schedule follow-up visits with their surgeon to discuss any concerns, assess the healing process, and have sutures or staples taken out as necessary.
Rehabilitation, to assist the treated region regain strength and function, physical therapy or rehabilitation activities may be recommended in some situations.
Monitoring and Imaging, to evaluate bone healing and graft integration, follow-up imaging examinations, such as CT scans or X-rays, may be carried out.
How long will the post-operative bone grafting treatment last?
The length of time needed for bone grafting following surgery can vary greatly based on a number of variables, such as the kind of graft utilized, the extent and location of the bone defect, the general health of the patient, and compliance with post-operative care recommendations. Generally speaking, the goal is to support permanent bone healing and integration while offering a long-lasting remedy for bone abnormalities.
After integrating well with the underlying bone tissue, bone transplants can last a lifetime for many individuals. In instance, autografts frequently offer long-lasting structural support because of their high success rate and propensity to integrate well with the recipient site.
It's crucial to remember that different people recover and integrate their bones at different rates. Even though some patients may see noticeable results from surgery in as little as few months, in certain instances the entire healing process might take a year or more. In order to track their progress and guarantee appropriate healing, patients usually schedule recurring follow-up sessions with their healthcare professional throughout this time.
In some circumstances, such severe bone loss or difficult surgical scenarios, several treatments or procedures can be required to maximize bone repair and long-term results.
Frequently asked questions about Bone Grafting
*The treatment pages provided on this platform are intended for informational purposes only and do not constitute medical or dental advice, diagnosis, or treatment recommendations. The information presented on these pages is not a substitute for professional medical or dental advice from qualified healthcare providers.
*By accessing and using the treatment pages on this platform, you acknowledge and agree to the terms of this disclaimer. If you do not agree with these terms, please refrain from using the treatment pages.